Outside each National Weather Service (NWS) office around the US stands for what a large white ball of soccer, enters roof metal scaffolding in many stories high. These simple simple spheres such as Ho-hum as a city tower, but tacked inside each of the most revolutionary tools of modern meteorology: Doppler Radar.
The national network of 160 high-resolution radar, installed in 1988 and has been updated in 2012, sending red to microwave to assist forecrops or other rains from events from the events of the blanks. And the network is especially inefficient with the arrival of tornadoes; It has a lot of high-time warning and reduced deaths. Doppler Radar has “changed how we issue warnings,” Ryan Hanrahan said, Chief Meteorologist at NBC Connecticut Stormticracrab.
But now meteorologists and emergency managers are increasing what can happen if any of these radars go offline, because of Cut the NWS created by Trump Administration or threats from groups selecting conspiratory theories about radars used to control the weather. “The loss of radar capabilities” returns to us in four decades, “said Jana Houser, a Tornado Researcher at the University of Storm.”
In support of science journalism
If you enjoy this article, think about supporting our winning journalism in Subscribe. By purchasing a subscription you helped to ensure the future of influential stories about the discoveries and ideas that make our world today.
How Doppler Rads works
NWS installations form a network called the next generation radar radar, or nexrad. Within every giant white whhere is a device like a larger version of a home tv dish, with a transmitter emitting the pulses of the electromagnetic spectrum. The pulses blast rainfalls, snowflakes, hail rain – what meteorologists collectively call hydromeors – and back to the antenna dishes. (Pulses occasionally erupts with bats, birds and even moving trains, which provide characteristic radar patterns that are often identified by experts.)
The power of returned signals sets experts who make a picture of the size, shape and energy in any rain – and this is what you see on a broadcad of the phone radar.
But Nexrad can do a lot, more than showing how fast it is raining. Within its space, each unit rotates and scans the sky, helps forecasters see what is happening in many storm systems. These vertical profiles can show, for example, if a tornado forms or a storm makes a downburst – a fast air blast. “Doppler radar is primarily allowing us to see in the clouds,” Hanrahan said.
And then there is a “doppler” part itself. The name refers to an event that is familiar to mostly, thanks to the electromagnetic waves’ acoustic counterpart. We all have experienced, always clear when we hear an emergency Sirden Siren Siren Pasyby: The pitch increases as the vehicle is approaching as long as it is running away. Similarly, the returning radar bounce from a droplet of rain or piece of litter leading to emitter has a shorter wavelength than an extended radar with a long wavelength. It allows radar that is useful to recognize the stiff circulation of a tornado.
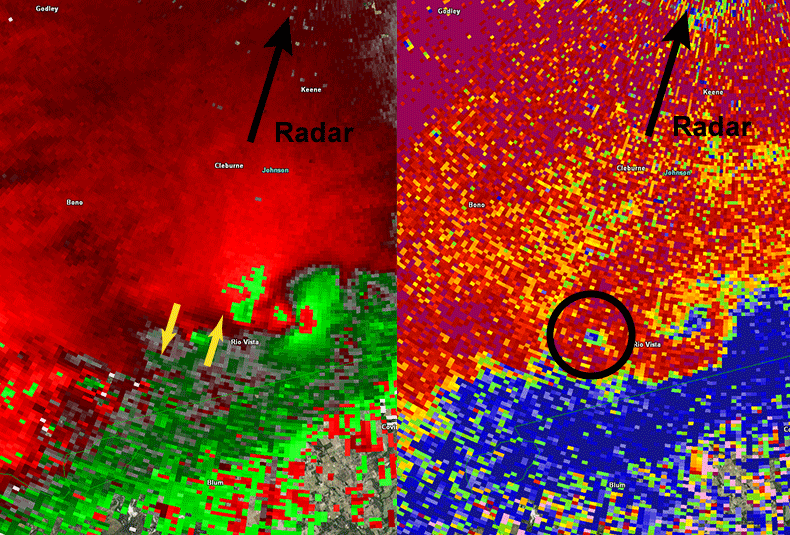
These two images shows how to help double-polarization of NWS forecasters find a tornado that makes damage. The left image shows how Doppler Radar appears the rotation. Between two yellow arrows, the red color indicates external air, while the green color shows the air entry, relative to the radar location. The correct image shows how the double-polarization information helps identify the garbage taken in the tornado.
The country’s radar system Upgraded to 2012 to include what is called double polarization. This means that the signal has the same vertical and horizontal oriented length length, which provides information about rainfall more than one scale. “A droplet droplet is almost perfect spherical, so returns the same amount of power on horizontal and vertical, while giant sleeping is like purified power than vertical.
Doppler Rads is dangerous? Can they apply time?
Doppler’s radars cannot impose any danger to people, wildlife or structures – and they do not affect the time.
With the electromagnetic spectrum, these are the parts that have more wavelengths such as gamma rays and radiation radiation that can easily damage the human body and damage DNA or our cells. Doppler radars emit pulses in long lengths in size with a baseball.
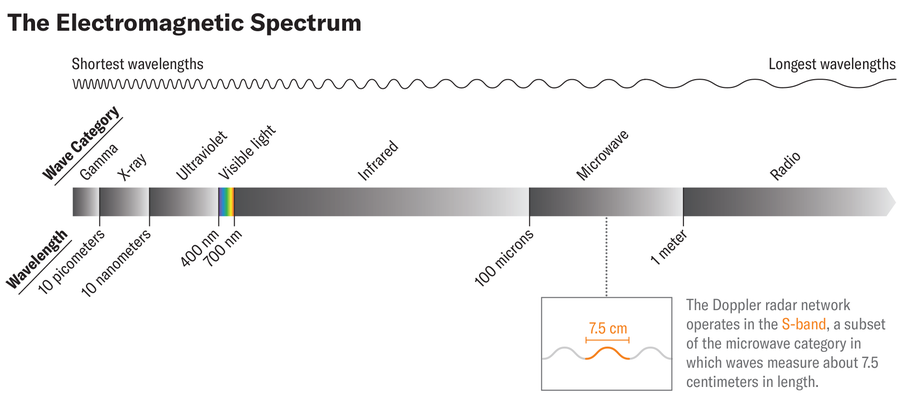
Struck by more concentrated radiation in microwave CAN harm; This is why microwave ovens have mesh screens that keep the rays from escaping. Similarly, you don’t want to stand directly in front of a microwave beam radar. Military radio technicians have been found these years ago when working on radar operations, University of California, Los Angeles, scientist Daniel Stoin said to a His regular youtube address. They “have experiences like the candy bar in their pockets then melt and then feel their skin so hot,” he said.
Similar to How a microwave oven worksWhen the microwave signal from a radar hits a hydrometor, water molecules flow and as an energy received for a focal point for the National Weather Service Operations Center. But “Microwave radiation is really not very powerful, and the whole point is that if you stand more than a couple dozen feet away from the dome it’s not even really going to affect your body, let alone the global atmosphere, let alone the global atmosphere,” swain adds.
At Radar’s antenna, the average power is 23.5 megawatts (MW) in force, Fay says. .-12 MW, Fay says. “Once you’re the mile, it’s never a dangerous value” in energy, the swain says his video.
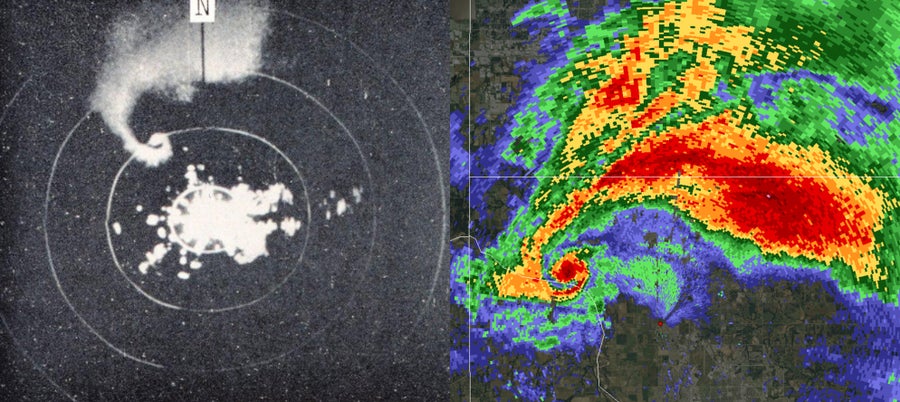
A supercell storm that makes an F4 tornado near Meriden, KS, in May 1960, as seen from the Topeka’s WSR-3 radar (nothing). A supercell storm that makes an EF5 Tornado in Moore, OK, in May 2013, as seen from a modern Doppler Weather Radar near Oklahoma City (TRUE).
And Doppler’s radars spent most of their time to listen for returns. According to the NWS, for each time of operation, a radar can spend a little like seven seconds sent the pulses.
The idea that the Doppler radar can be controlled or affects the period “a long conservation consultancy (theory) with real years,” as the swain of his video. It has been resurrected to the threats of National Oceicic and Atmospheric Administration Radar System from Antigrovernment Militiaphor, as reported to cnn. the WASHINGTON POST reported that group builder says that its members have implemented “Attack simulations“On sites to destroy the radars, – if the group believes” weapons during the Teads exercise – and identify the NWS teams in the NWS teams.
“NOAA knows recent threats against Nexrade radar sites and work with local and other monitoring authorities in a request American American.
What happens when weather radars go offline?
Noaha’s radars are duty in 12 hours a day, seven days a week and 365 days a year from 1988 (with short progress and upgrades). “Wonder what worklors are these radars,” Hanrahan said.
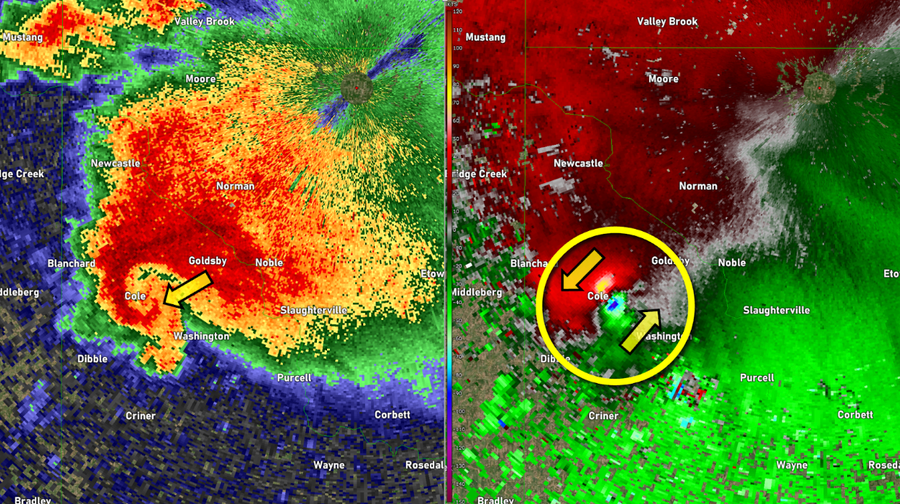
The image of the left shows a Rescastored radar radar image producing several tornadoes on April 19, 2023, near Oklahoma City, ok. Hook forms currently often indicate rotation within the storm. The image to the right performance speed of information corresponding to the reflection image. Very windy air (green colors) The next strong wind (chamanyhirightly red / yellow color). This very strong entry / outbound “advance” indicates the very strong rotation of a tornado.
But they need to be that each maintenance because of all many transfers that are necessary to operate it. And to cut Trump administration of NOAA staffing and frozen some expenditure, “We just took many radar maintenance technicians, and we took the budget to fix his video. “Most of this works well now. The question is: What happens once they get down, once they need to heal?”
This is the probability that it is the possibility that most experts in time, especially when breakdowns occur in any kind of serious weather. “Radars are key instruments to issue tornado warnings,” as home at home at Ohio State University. “If a radar goes down, we are more than what is a bigger picture.”
And for most of the country – especially to the west – no less overlap in areas attached to each radar, which means other sites do not work without a neighboring radar. Hanrahan said the information provided by radares could not be maintained, and 2012 upgrades meant with the eyes of a tornado this is happening today. “










