The beginning of June marked the start of the Hurricane period in Atlantic, the six-month period when strong storms could cook at sea and then break into the ground. Among the hazardous consequences of storms Storm runswhere water can easily rise over the normal level of tiding to the beach. These dangerous events can cause flooding and extracting and moving homes and other structures. “The water is very strong,” Heather Nepaul, a meteorologist of the National Oceicic and Atmospheric Storm of Atmosphere in Miami. “It will be a fatal state.”
Surges occur when the Strong air in a storm Talk to the oceans of the ocean, which focuses on the water ahead of the storm. As storms that went to the beach, it traveled to a more powerful sea, and the water it brought was homeless to the ground.
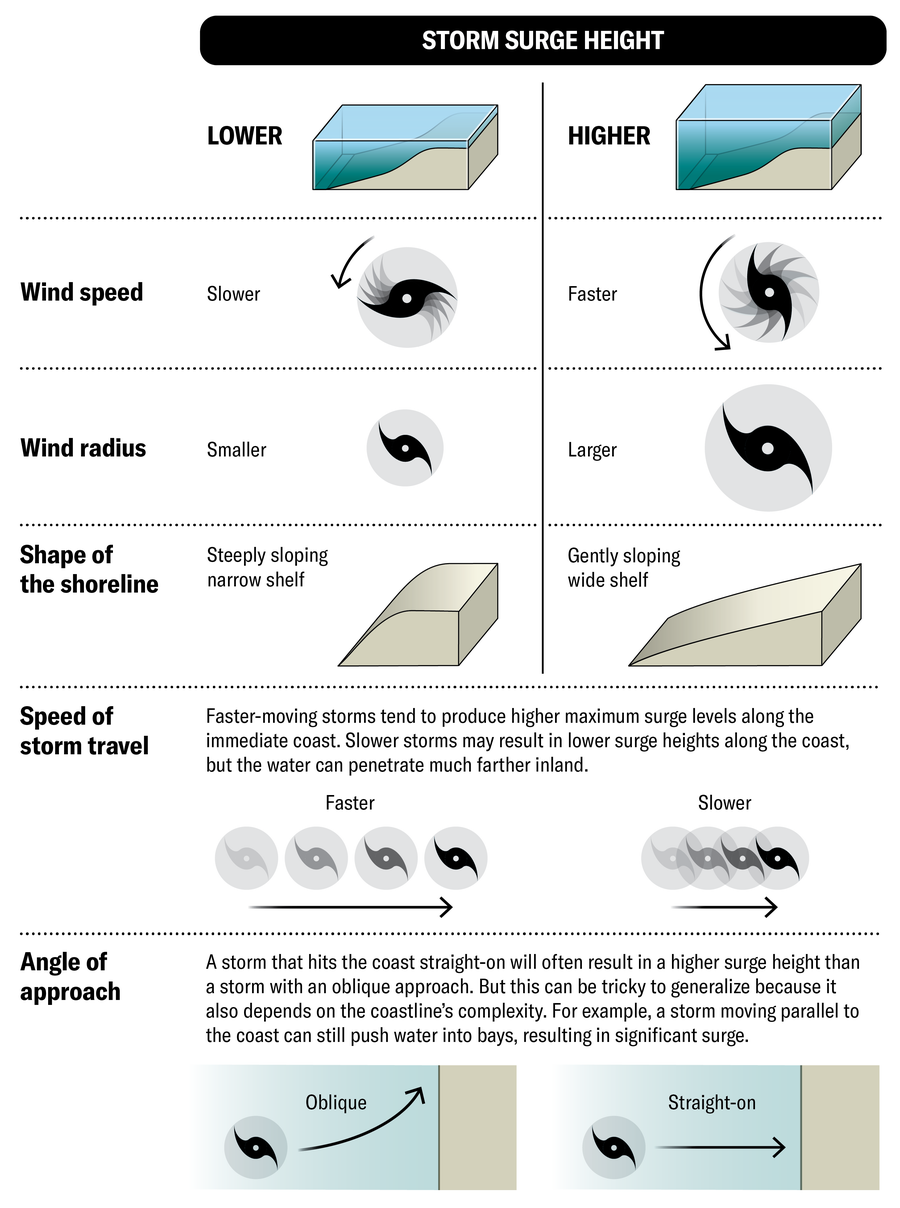
How severe drain depends on many reasons, including beach traits and energy, size and angles of storm method. Overall, even if not always, more powerful and more stormy makes the higher storms of energy.
In support of science journalism
If you enjoy this article, think about supporting our winning journalism in Subscribe. By purchasing a subscription you helped to ensure the future of influential stories about the discoveries and ideas that make our world today.
As the climate smits, Storms become more intenseand Sea level rises. Both of these effects are likely to worsen Storm Surges. The areas on the coast of thunderstorm into the storms will experience serious effects, and areas less vulnerable today may be more risky.
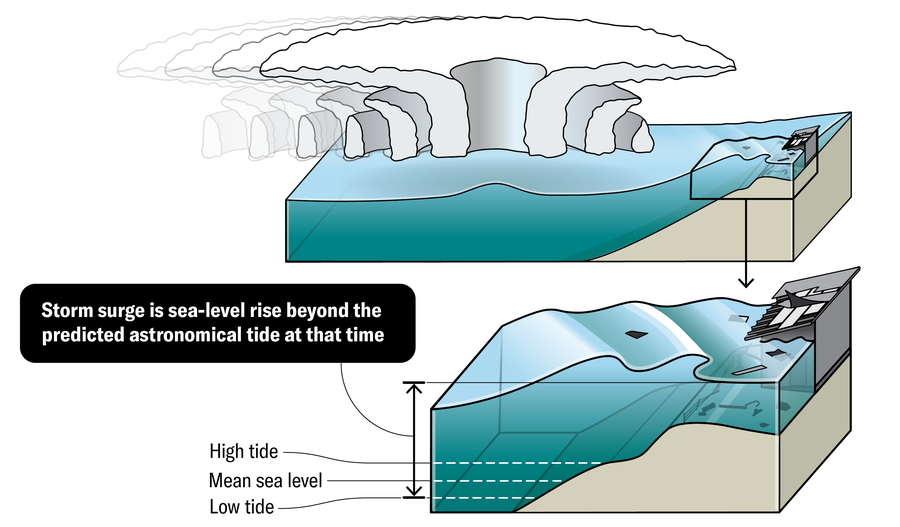
How it works
The majority of a strong storm is caused by air pushing the water on the beach. A small part of the impact, however, comes from the low atmospheric pressure within a storm, which decreases the amount of low sea force, which has developed water level.
While the strong storms, progresses, the wind spirals pull the ocean water to its center. Upon arrival on the ground, excess water ran over the coast above and beyond the normal level of water drain.
Variables that affect the long storm
The burden of storms is hard to predict because it depends on several variables: the speed of air associated with the storm, and the speed of powerful storms, and the specified storms of the beach where it is facing.
Storm Surge Regorm
These charts, based on National Hurricane Center Country Storm Surge RegormDisplay the potential amount of the US Atlantic beach for hurricanes in different severity. Storms are categorized on a scale from 1 to 5 to the force of their winds, with 5 worse. The drains can affect the beach but the locations of many miles on the ground.
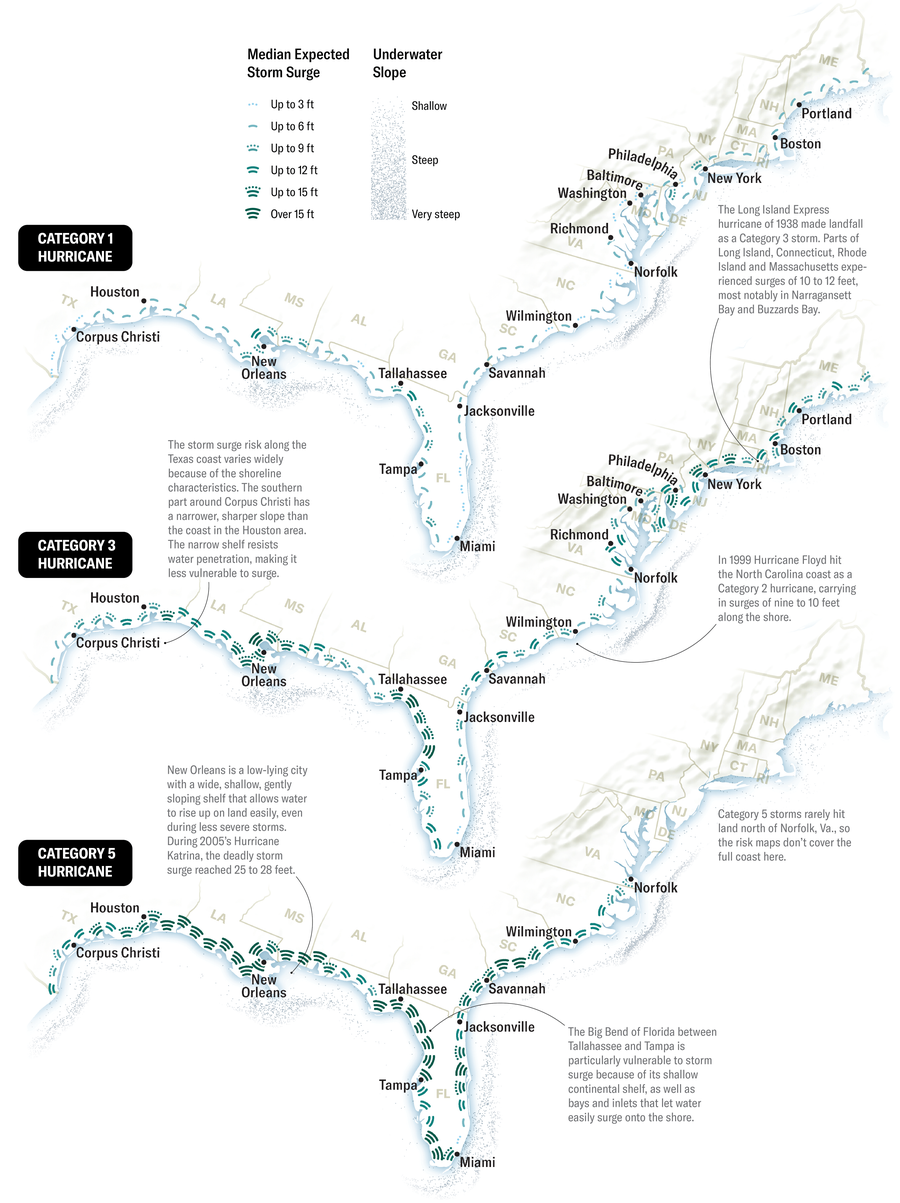
Daniel P. Huffman; Source: “A national view of Storm Surger Regorm and Flow,” by Brian C. Zachry, William J. Booth and Tarate, Climate, Tapha, Toldy. 7, No. 2; April 2015; via www.nhc.noaa.gov/ ofalsurge (Map of data)










