Papovavirus is a term that unites viruses in the papilloma (PA), polyoma virus (polyoma (polyolating agents. The name “Papova”, “in” the formation of the tumor. In history, these viruses are classified under the family PapovaviridaeBut this classification is no longer recognized. Viruses are currently divided by two separate families: Human papillomaviruses (HPV), and man polyomaviruses.
- Papillomaviridae: The Papillomavoruse man’s family (HPV)
- Polyomaviridae: The family of polyomaviruses in man
The agent yard is classified under Polyomaviridae Family, which is a group of viruses with some traits. Both papillomaviruses and polyomaviruse are DNA viruses Tramuses of NUBOmean they are lacking in an envelope. This attitude makes them stronger in the environment and easily sent by direct or indirect contact.
Human Papillomaviruses (HPV)
Papillomaviruses of the person (HPV) a group of more than 200 related viruses mainly in SKIN and mucous membranes, like a genitals, mouth, and throat. HPV infection occurred in Dividing the epidermal cells or Basal Layer Cells Of the skin, where the virus enters cells and begins to waste. HPV Best host-specific and Tissue specificallymeans it typically affects a species and target specific types of tissue.
One of the HPV study challenges is that it cannot be culture in laboratory conditions. it Just grow up in the stratified squamous epithelial cellswhich is hard to grow except the body. This means traditional cell culture techniques for the island of viruses cannot be used in HPV. Thus, detection In HPV infections depends on other methods, such as Immunoassays and Genetic Prices.
HPV check
Since HPV cannot be culture, detects focus on identifying genetic materials of virus in infected cells. This can be through ways to want DNA Hybridization (PCR, Southern Blot Glory) or In situ hybridization. Mucosal smears (eg, from cervix, vagina, or anus) usually used for testing, and Pap Smear tests Always attach HPV test to determine HPV presence and identify specific strains.
A famous limit is that, as now, have No test available to find HPV in male steps. However, well documented that men can improve Genital Warts Due to HPV infection, even if cancer progress is rarely compared to women. Men are considered to be vectors to deliver the HPV, including the spread between Women who have sex with women (WSW).
Types of Papillomaviruse in man HPV
HPV types are classified based on their Tissom Troopismor preference for infection of certain types of tissues. HPV types are classified into two wide groups:
- Cutaneous kinds: It is mainly causing skin and cause common warts.
- Mucosal types: This is the cause of mucous membranes and is associated with Kinatonasan Warts, as well as Cervical Cancer.
Among muucosal types, above 40 types of HPV passed by sex, and it was appointed to Types of genital. These types are multiplied based on their association Cancer of genitals As:
- Types: HPV 16, 18, 18, 33, 45, 56, 58, 58, 59, 68 is associated with an increased risk of Cervical Cancer and other cancers.
- Different risks: HPV 6 and 11 are mainly responsible Genital Warts and unusual causes cancer.
- Intermediate-risgum types: These types are associated with lowest dangerous wounds but not as often as commonly linked with cancer as high-risks.
Cervical Cancer and HPV
One of the most important medical concerns associated with HPV is the strong association Cervical Cancer. Cervical Cancer is the third most common woman cancer in the world, following CHEST and Colorectal Cancers. It is mainly caused by infection with high-risk types of HPV, especially HPV 16 and 18be responsible for part 98% of cervical cancers.
In fact, above 50% of women Contract a genital HPV infection within 2 years to being sexually active, and estimated to be 80% to women who will be affected by the HPV in their lives. However, most infections are transferring and asymptomatic, and the immune system cleanses the virus without any long-term side effects. In some cases, especially with high-riser HPV types, infection will continue and can lead to Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)which is a leading cancer.
HPV and other cancers
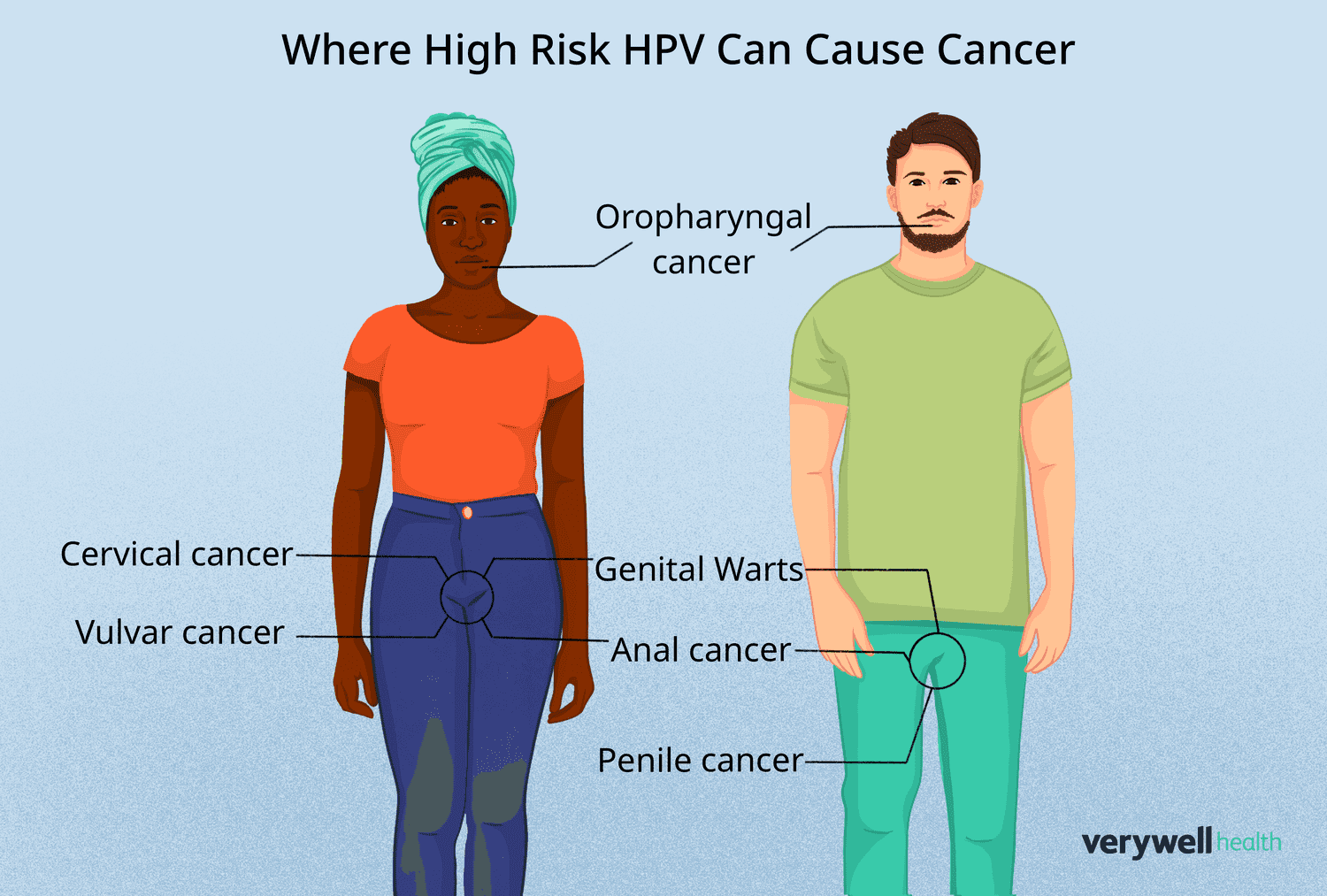
while Cervical Cancer is the best known cancer associated with HPV, other cancers also involved in the virus. Anal cancer becomes more common, especially with men who have sex with men (Msm) and individuals with HIV. Although anal cancer is not yet common than cervical cancer, its incident increases.
HPV can also cause cancers in oropharynxincluding throat,, tonsilsand TONGUEespecially with individuals who share oral sex. Studies show that an increased number of oral and vaginal sex partnerslack of Using condomsand Poor Dental Hygiene Correlate to a higher risk of development of oropharyngeal cancer related to HPV.
Reasons for risk for cervical cancer
Many reasons for risks are associated with Papillomavalus Papa infections and the consecutive development of cervical cancer. This includes:
- Number of sexual partner: Women with many sexual partners higher risk of contracting HPV.
- Age of first intercourse: Early start of sexual activity increases the risk of exposure to HPV.
- Sexual activity of associated men: Companion men with many sexual partners can increase HPV transmission risk.
- Failure to use Barrier Contraception: Lack of condom use increases the possibility of HPV transmission.
- Smoking: Tobacco use degrades the immune system and adds easy HPV infection.
- Using oral contraceptive: Long use of identity pills can increase cervical cancer risk, especially with females smokers.
- Many pregnancies: Women who have many pregnancies can have a higher risk of developing cervical cancer.
- Immunosuppression: Individuals with weak immune systems, such as those with HIVs, especially reduced HPV infections.
Diagnosis of HPV
Diagnosis of HPV Infection often involves a combination of ways:
- Biopsy and hisology: Biopsy samples from abnormal tissues are assessed to determine changes characteristic of HPV infection.
- Pap Smear (Pap): This is a widely used screening tool involving collecting cells from the cervix. If the HPV is suspected, further attempts such as Try DNA (PCR, South Blot Hybridization) or In situ hybridization can be held.
Benign loions caused by hpv
Many types of HPV infections lead to Benignle Lyons That does not cause cancer but uncomfortable or causing cosmetic concerns. This includes:
- Common warts (Verruca vulgaris): characterized by moderation, raised surfaces, commonly found in hands, knees, and feet.
- Flat Warts (Verrucae Plantae): Gently and flatter more than common warts, it is usually visible to children.
- Butcher warts: With butchers, but the reason for their occurrence of this occupation is not fully understood.
- Genital Warts (Condylomata acuminata): Due to HPV type 6 and 11, these warts are found in anal and anal areas. They are usually things but uncomfortable and causing complications during childbirth.
Malignant or potentially harmful wounds
HPV can also bring malignant or potentially harmful woundsincluding:
- Pwowooid papulose: More Papules in Penis or Bulka similar Bowen’s pain. These wounds can be a malignant.
- Intraepithelial dysplasia: Abnormal changes in epithelium, commonly called cin (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia) in cervix, Vain (Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia), and Vin (Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia). The worst form of dysplasia, Cin 3, involves all the layers of epithelium and have a long time to advance invasy cancer.
Vaccination and Avoid
The best way to prevent HPV related diseases vaccination. The HPV vaccine is most effective if served before starting sexual activity. the CDC HPV vaccine recommended for individuals between the ages of 11-12 (Although vaccination can start at age 9). art 3-Dosis Regimen Usually used:
- First dose: Given to first appointment.
- Second dose: 1-2 months after the first dose.
- Third dose: 2 months after the second dose.
Existing vaccines with:
- 2VHPV (Cervarix): Target of HPV 16 and 18 (approved for women only).
- 4VHPV (Gronsasil): Target types of HPV 6, 11, 16, 18 (approved for men and women).
- 9vhpv (Gardasil-9): Target 9 types of HPV (6, 11, 18, 18, 31, 35, 52), and 58), and men.
These vaccines prophylacticmeans that they can prevent infection but not treat existing infections.
Treatment and Management
Now, nothing Antiviral drugs available to treat HPV infections. Vaccines offer protection against Pre-cancers and non-invasive cancers such as cervical pre-cancer, but they do not heal active infection. Treatment for HPV related Warts And wounds often include topical treatments, cryotherapy, or surgical removal.
Finally
Papillomavirus person infections (HPV) is a global public health issue, with many contributions to the development of cancers such as cervical cancer. While no drugs for HPV infections, preventing measures such as vaccination shown to reduce the incident of cancers related to HPV. Comprehensive education, early analysis, and vaccination is critical to reducing HPV health weight.










